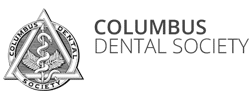
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHNES) reported the most recent statistics on the prevalence of adult periodontal disease in the United States from 2009-2014. Data were collected from over 10,000 U.S. adults over the age of 30. The mean age was 50.8 years, with a female: male ratio of 51:49% and a mean of 24 teeth present per subject. Standard periodontal examinations were conducted using the American Academy of Periodontology format.
 The following findings are some of the highlights:
The following findings are some of the highlights:
- Approximately 42% of the dentate American adults 30 years and over have periodontal disease.
- 7.8% have severe periodontal disease.
- Severe periodontal disease was most prevalent in the age group of 65 and older.
- Periodontal disease was most prevalent among the Mexican-American, followed by non-Hispanic blacks
- The prevalence of periodontal disease increased with increasing poverty level.
- Periodontal disease is more prevalent among current smokers, people who did not regularly floss, and those that have not visited the dentist within the past 6 months
- Periodontal disease significantly co-occurred with diabetes and increasing number of missing teeth.
In conclusion, periodontal disease is highly prevalent and a major health problem among U.S. adults. This NHNES study provides the most comprehensive and up-to-date estimates of the incidence of periodontal disease in the adult U.S. population. This information should be useful in the awareness, prevention, treatment, and maintenance of periodontal disease.
 Dr. Sakamoto
Dr. Sakamoto
 Dr. Mannava
Dr. Mannava
 Our Team
Our Team
 FIRST VISIT
FIRST VISIT
 PATIENT FORMS
PATIENT FORMS
 DENTAL INSURANCE
DENTAL INSURANCE
 POST-OP INSTRUCTIONS
POST-OP INSTRUCTIONS